Humidity Sensors
Last Updated:
- English
- Türkçe
Humidity Sensors
The growing demand for environmental control for a variety of chemical molecules has led to considerable interest in the research devoted to the development of new materials for sensor devices. Since humidity is a very common component in our environment, measurements and/or control of humidity are important not only for human comfort but also for a broad spectrum of industries and technologies. The constructive design of a good humidity sensor is a rather complicated topic, because high performance humidity sensors claim many requirements, including linear response, high sensitivity, fast response time, chemical and physical stability, wide operating humidity range and low cost.
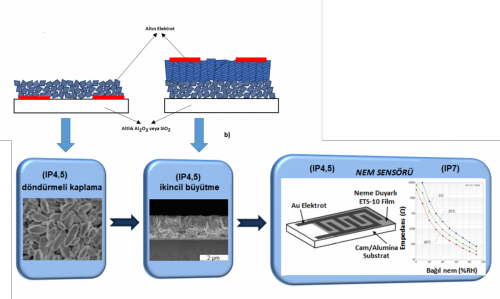
Zeolites and zeo-type materials are known for their well-defined porous structure, moisture holding capacity and ionic conduction properties. Therefore, a study is done to investigate humidity sensing properties of microporous titanosilicate and vanadosilicate thin films. Two different zeo-type materials with different type of quantum wires in their structures (i.e.,–Ti-O-Ti-O-Ti- and –V-O-V-O-V- in the structures of ETS-10 and AM-6, respectively) were produced and the humidity sensors by using these types of films were fabricated for the first time. Developed humidity sensors are examined by impedance spectroscopy method. By this means, conductive properties of the films dependent on the relative humidity will be revealed. The results showed that stable, sensitive, and cheap resistive type humidity sensors that operate in a wide range of relative humidity can be designed by using titanosilicate ETS-10 and Vanadosilicate AM-6 films.